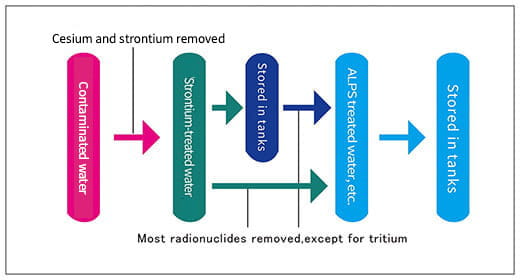
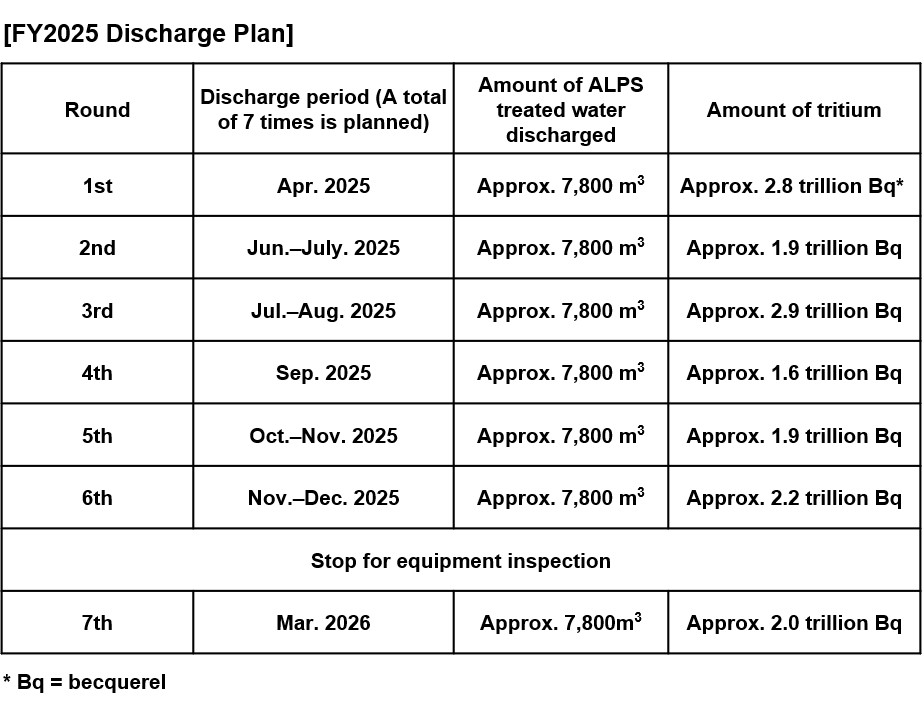
In FY2025, approximately 54,600 m
3 of ALPS treated water (total amount of tritium: approximately 15 trillion Bq) will be discharged into the sea in 7 times, as in FY2024.
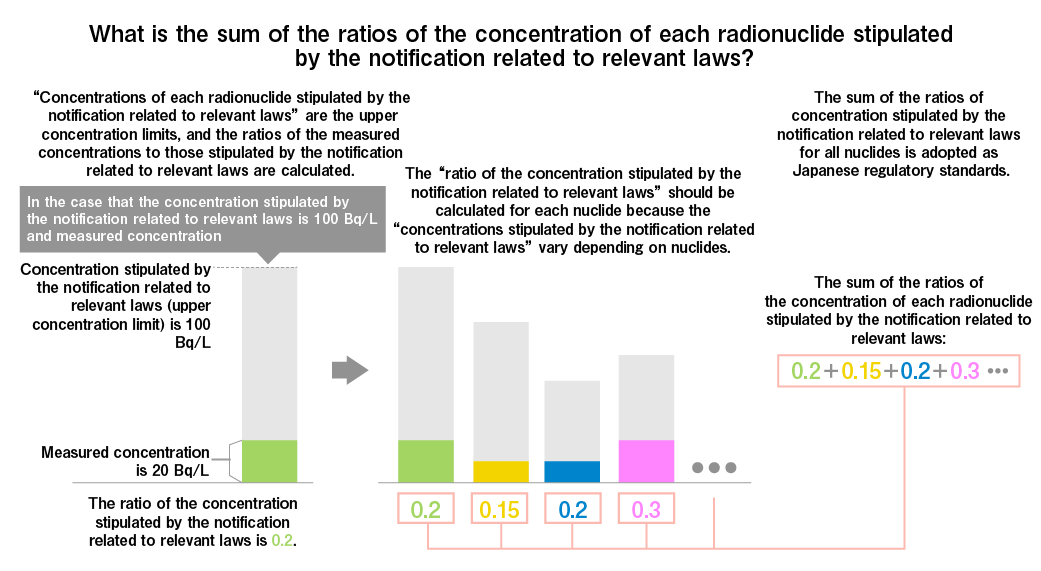
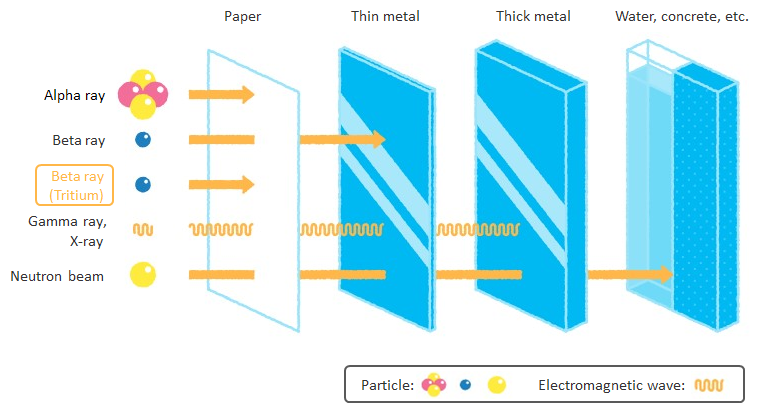
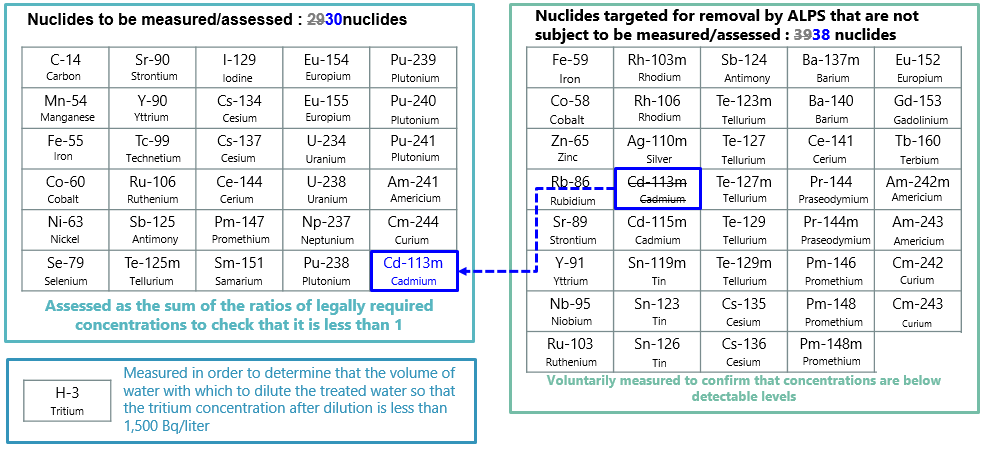
As with previous discharges, before each discharge of ALPS treated water, we will confirm that the concentrations of radioactive materials other than tritium meet the national regulatory standards for discharge into the environment (The sum of the ratios of the concentration of each radionuclide stipulated by the notification related to relevant laws
* is less than 1.) Tritium will be diluted before discharge, and tritium will be discharged in compliance with the government policy that the tritium concentration be less than 1,500 Bq/L, which is 1/40 of the national regulatory standard (60,000 Bq /L) and approximately 1/7 of the WHO’s drinking water quality guideline (10,000 Bq/L).
In addition, from the perspective of ensuring safety over the medium to long term, an equipment inspection is scheduled between the 6th and 7th discharges also in FY2025.
We will continue to prioritize safety in the discharge of ALPS treated water into the sea with safety as our top priority.
Click here for details of the FY2025 discharge plan
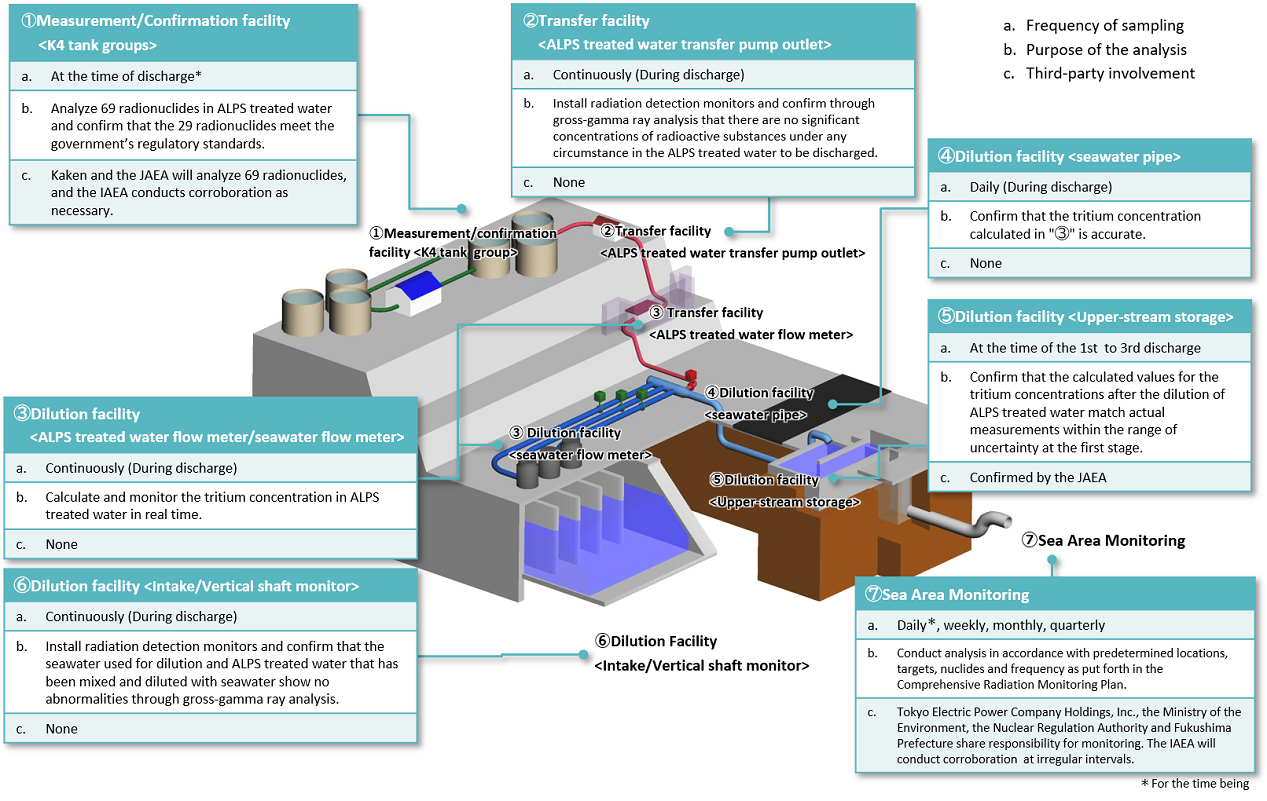
On the TREATED WATER PORTAL SITE’s top page, you can check the status of discharges into the sea. In addition, on the Dilution/Discharge Facility Conditions page, you can see real-time updates on the tritium concentration of the ALPS treated water prior to dilution, the amount of ALPS treated water transferred to the dilution/discharge facility, and the amount of seawater pumped up for dilution.
Click here for the TREATED WATER PORTAL SITE “Dilution/Discharge Facility Conditions” page
* The sum of the ratios of the concentration of each radionuclide stipulated by the notification related to relevant laws: The Japanese regulatory standards for nuclear facilities, which are based on the recommendations of the ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection), specify the upper concentration limits (concentrations stipulated by the notification related to relevant laws) for radioactive materials that may be discharged into the environment for each type of radioactive materials. The sum of the ratios (proportions) of the concentrations of all radioactive materials contained in liquid or gas that are discharged into the environment to the "concentrations stipulated by the notification related to relevant laws" is adopted as Japanese regulatory standards. The concentrations stipulated by the notification related to relevant laws in liquids are specified as the concentrations at which the average exposure dose from drinking approximately 2 liters of liquid containing the radioactive material every day from birth to age 70 would reach 1 mSv per year, the upper limit of exposure dose for the general public in Japan based on the ICRP recommendations.
[Reference] The exposure dose from natural radiation (annual average, in Japan) is approximately 2.1 mSv.